The entire human body, including the head, face and neck, forms muscles. And the contours of a particular zone of the human face depend on the tone in which they are located. In order to maintain the elasticity and elasticity of the muscular skeleton for a long time, you should understand how to work with them correctly, you need to study photos with descriptions and be able to read muscle structure diagrams.
- Why do we need anatomical knowledge in cosmetology
- Facial muscle anatomy
- What shape do facial muscles have
- Where are the muscles and how are they attached
- How to shrink
- Where is platism
- Massage lines and facial muscles – relationship
- Muscle groups
- Facial muscles and emotions
- Age-related changes in facial muscles
- What facial muscles inject Botox
- Video on the topic: facial muscles, photos with descriptions and diagrams
Why do we need anatomical knowledge in cosmetology
Modern cosmetic procedures cannot be performed without basic knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the skin.
This information enables the cosmetologist to work correctly on age-related changes in the skin, to qualitatively improve its general condition and to conduct timely work with the facial muscles, acting on them with the help of massage movements during cosmetic procedures. 

The structure of the muscles of the skin of the face, the study of their descriptions from photographs and diagrams – this is the basic knowledge of anatomy. Without them, no cosmetologist will be able to competently massage, inject Botox under the skin of the face without negative consequences, or perform the microcurrent therapy procedure.
Facial muscle anatomy
What shape do facial muscles have
The facial muscles look like flat elongated bundles with a very thin muscle part.
Where are the muscles and how are they attached
This muscle group is located in the subcutaneous connective tissue of the facial part of the head. They, unlike the muscles located in other parts of the human body, do not have double attachment to the bones of the skeleton, but are woven at one end into ligaments. 



The exception is a small group of 4 muscles, which is located on the lateral surface of the head and provides the process of chewing food. The facial muscles are often paired, with the exception of the circular muscles of the mouth, nasal and cranial. In addition, the muscles are classified by depth. Allocate deep, middle and superficial muscles.
How to shrink
The activity of the facial muscles is always coordinated by the central nervous system. The brain, receiving a signal about any process taking place from outside, transfers it to the facial muscles, and those, in turn, translate the information received into the language of muscle contraction and display it on the person’s face in the form of any mimic movements.
Any muscle movements are always an accurate reflection of all kinds of nerve impulses.
With nervous diseases, injuries, infections, muscle contraction is impaired. These changes can be congenital, permanent and temporary. The most serious disease is facial paralysis. Because of it, the muscles lose their ability to completely close their eyes and jaws.
Where is platism
Platism is a superficial thin layer of neck muscles that is responsible for its beauty and overall appearance. It is located immediately under the skin and fuses tightly with it.


Despite this fact, platism does not participate in movements carried out by the head and neck, and strains only with strong physical exertion or with acute emotional experiences: for example, at the time of violent anger or severe physical pain, thereby playing a significant role in facial expressions. In many ways, platism is different from all other muscle groups.
Platism is more susceptible to all kinds of changes and a rapid loss of elasticity, therefore, its condition requires timely and high-quality preventive care.



 Do not miss the most popular article in the rubric:
Do not miss the most popular article in the rubric: Facial massage according to the Japanese doctor Asahi Zogan.
Massage lines and facial muscles – relationship
Muscles for the face are a kind of skeleton that supports the skin in good shape, while keeping it supple and supple. And massage is that manipulation that has a beneficial effect on them, further tightening the skin on the face itself. Massage makes the skin on the face even more fresh and beautiful, helping to get rid of acne and bumps, creating a chiseled contour of the face itself. 

This procedure is done strictly along the massage lines – certain directions of movements that the cosmetologist conducting this procedure adheres to.
The direction of the massage lines: 

- from the middle of the chin along the jawbone;
- from the corners of the lips to the bottom of the ears;
- from the back of the nose in the direction of the temples in both directions;
- from the wings of the nose to its back;
- from the nose to the hairline;
- from the interbrow space to the temples and hair.
Massage lines coincide with the direction of the lymph flow, and with certain manipulations contribute to its acceleration. This, in turn, has a good effect on the general condition of the skin and helps rid the body of excess toxins and toxins, and remove swelling.
Muscle groups
A person has more than a hundred facial muscles located on the head and neck. Details of each of them can be seen in the photo with a description and diagrams.
Anatomy subdivides all these muscles into several conditional groups:
- mimic;
- oculomotor;
- chewing; the oral cavity; language
- muscles of the neck.

 Some of the facial muscles can belong to different groups at the same time.
Some of the facial muscles can belong to different groups at the same time.
Chewing muscles
Chewing muscles provide the performance of chewing movements.
These include:
- muscles of the head (temporal, chewing, lateral, medial pterygoid muscles);
- muscles of the neck, the location of which is higher than the hyoid bone (maxillary-hyoid, chin-hyoid and biceal muscles).
This group of muscles has a minimal effect on the appearance of the face.
The chewing muscle, which is responsible for raising the lower jaw of a person while making sounds or eating food, is constantly in good shape and does not need additional exercises. However, it tends to undergo spasms due to increased tooth compression, and this negatively affects the blood supply to this area of the face and activates the aging process in it.


The same can be said of pterygoid chewing muscles, the main purpose of which is to grind coarse foods. Care for this muscle group should be competent in order to contribute to the formation of the correct oval of the face and prevent further formation of deep wrinkles in the lips.
Facial muscles
The functionality of facial muscles consists in the formation of emotional manifestations on a person’s face due to a certain extensibility of the skin and the formation of folds that appear in the transverse direction, relative to muscle contraction. The more emotional a person is, the higher the risk that facial wrinkles will quickly appear on his face and neck.


The facial muscles are divided into muscles:
- upper front part;
- middle part;
- lower face and neck.
The first ones, when stretched, form vertical wrinkles on the forehead, horizontal folds on the bridge of the nose and the so-called crow’s feet under the eyes, the second ones create the effect of “hollow cheeks”, deepen the nasolabial folds and wrinkles under the eyes, and in the mouth.


Muscles of the third group – lower the corners of the lips and protrude their lower part forward. A high-quality study of the entire muscle zone will completely remove the listed disadvantages and make the skin texture smoother, more even.
Cervical muscles
Cervical muscles are divided into 3 subgroups:
- superficial muscles of the neck;
- hyoid muscle
- deep neck muscles: front, middle and back scalene muscles.


The cervical muscles, unlike the mimic ones, have 5 fasciae (the so-called connective tissue membranes that cover the muscles themselves):
- superficial fascia;
- own fascia of the neck;
- scapular-clavicular fascia;
- intracervical fascia;
- prevertebral plate.


Muscular imbalance and spasm of the muscles of the neck always provoke the development of sagging skin on this part of the body and contribute to the development of wrinkles and folds on the side of the neck, the formation of transverse folds and the second chin.
Other classifications
In addition to the above muscle groups, there are so-called muscles of the internal organs, such as the tongue, palate, middle ear and eyes. 
 These muscles also take part in shaping the appearance of the face and facial expressions. They can be considered in more detail in the photo with descriptions and diagrams presented in the article.
These muscles also take part in shaping the appearance of the face and facial expressions. They can be considered in more detail in the photo with descriptions and diagrams presented in the article.
Facial muscles and emotions
Each muscle belonging to the mimic group coordinates the expression of an emotion:
- For example, the frontal raises eyebrows and forms horizontal folds of the forehead, thus expressing surprise on the human face;


- The circular muscle of the eyes helps to squint at the moment of fright, roll your eyes up or, conversely, lower your eyes, thereby helping to express embarrassment or misunderstanding. At the same time, this muscle never works in a duet with the frontal;
- The large and small muscles of the cheekbones help reproduce a smile on the human face, lifting the edges of the lips up;
- The muscle responsible for lowering the corners of the mouth, on the contrary, is activated when a person experiences negative emotions;
- The muscle of laughter allows you to stretch the corners of the lips in a horizontal direction and forms “dimples” on the human face with a smile;


- The circular muscle of the mouth is included in the active work when an air kiss is sent;
- If a person experiences emotions such as disappointment, doubt or anger, then the chin muscle comes into play, which slightly lifts and pushes the lower part of the face forward;
- If you feel fear, disgust, or other negative emotions, the superficial muscle of the neck is activated, which tenses, doing its job.
In total, about 1200 different combinations of muscle contractions have been revealed in nature, reflecting one or another emotion on the human face.
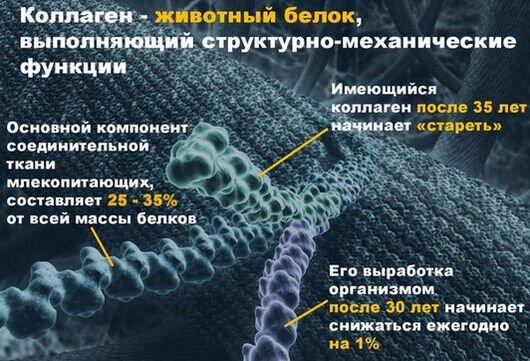
Age-related changes in facial muscles
Over the years, muscle facial tissue loses its elasticity and lengthens. The format of such metamorphoses depends on how the muscles behave in different conditions: in a stressful situation, during a rest or work process, or when talking to people.
Such factors as life style, self-care gallon and heredity have a considerable influence.


In those areas where the muscles are not sufficiently firmly fixed with one part of them on the skin membrane, so-called fatty hernias form over time due to pulling of the ligaments under the influence of the arising load. And where the ligaments are still able to hold the muscles of the face, folds and creases appear. 

There is an opinion that age-related changes in the facial muscle tissue occur due to tone, elasticity and its increased relaxation, but in fact the point here is different – in the constant tension of the muscles that cause spasms. Facial skin with an increased contraction of muscles falls in a fold, changing the relief and structure of the skin. 





For example, a spasm of the forehead muscle tissue leads to the formation of transverse and horizontal lines in this area of the face, an increased tone of the circular muscle of the eye leads to the formation of wrinkles in the eye area, and contraction of the muscles of the middle facial part leads to the appearance of nasolabial furrows.



 Do not miss the most popular article in the rubric:
Do not miss the most popular article in the rubric: Face fitness for lifting the face contour, rejuvenation, muscle tone. Master class from Elena Karkukli
What facial muscles inject Botox


The introduction of Botox is aimed at eliminating facial wrinkles and restoring smoothness to the skin texture. Injections of botulinum toxin (purified natural protein) are performed by the cosmetologist subcutaneously or intradermally into the facial muscles.
These are the muscles where it is necessary to reduce the susceptibility to incoming nerve impulses in order to slow down the process of deepening wrinkles in the skin and tighten sagging skin.
In the best way, botulinum toxin injections show their effect in the following muscles:
- in platism;
- in the muscle that lowers the corners of the mouth;
- in the circular muscles of the mouth and eyes;
- in the chin muscle;
- in the nasal muscle;
- in the frontal muscle;
- in the muscle of the proud and the muscle that wrinkles the brow.
The amount of the drug for each muscle zone is determined by the cosmetologist, who is carrying out the procedure for introducing Botox under the skin, individually. The maximum effect of “solidification” of the facial muscles is observed for 3-6 months after the injection. 

As soon as the muscles begin to make their first contractions, after this period of time, the action of injections of botulinum toxin under the skin lasts for about another 6 months.


The muscles of the face (a photo with a description and schemes can be viewed above) should be studied from the photographs and schemes presented. Schemes are presented in American and in Latin. On them you can see a detailed description of where this or that group of facial muscles is located.
If you know the exact location of the facial and cervical muscles and get acquainted with the principle of their work, having figured this out by studying descriptions, photographs and diagrams, you can slow down the aging process through the subsequent competent stimulation of certain muscle groups, while maintaining skin elasticity and youth for a long time.
Video on the topic: facial muscles, photos with descriptions and diagrams
How to tighten facial muscles and make an ideal oval:
Scheme of self-massage of the muscles of the face Renaissance:
Description of the procedure for injecting dysport into the muscles of the face:
Facelift. Photos before and after surgery: